2020-08-31 by Quick Biology Inc.
Extrachromosomal DNA (ecDNA) is any DNA that is found off the chromosomes. In early Feb, we discussed one research work led by UCSD and Stanford. By integrating RNA-Seq, ATAC-seq and 4C-seq etc, they revealed extrachromosomal circular DNA (eccDNA) is common in cancer cells, has a loose chromatin structure, genes encoded in eccDNA are most highly expressed.
In Aug 17 2020 Nature Genetics, the same groups systematically analyzed ecDNA in cancers, or blood an normal tissue (ref1), novel findings include 1) build up AmpliconArchitect computational pipeline that can discover ecDNA events just using whole genome sequencing. The authors have evaluated the accuracy of AmpliconArchitect’s prediction by the FISH probe and CIRCLE-seq (circularization for in vitro reporting of cleavage effects by sequencing) (Fig.1); 2) Data analysis of 3,212 cancer patients shows oncogenes are highly enriched on amplified ecDNA (Fig.2); 3) Patients whose cancers carried circular exDNA (eccDNA) has significantly shorter survival (Fig.3). We believe “AmpliconArchitect” will be a great toolkit for implementing into any ecDNA profiling studies (see details in Fig.1 Legend); Their results such as ecDNA’s frequency in different cancer types, distribution, and clinical impact will be a principal data, aid further studies in ecDNA cancer genomic field.
Fig. 1: AmpliconArchitect Tool and Evaluation of its ecDNA predication accuracy. a, Schematic representation of the four classification categories. All DNA regions with a CN of 4 or greater than ploidy and comprising at least 10 kb were classified using a hierarchical scheme based on the AmpliconArchitect amplicon reconstruction and the types of discordant breakpoint edges in the region. The four categories are defined as follows: linear amplicon, that is, an amplicon that contains amplified segments with either no discordant edges or with edges suggesting deletions smaller than 1 Mb; heavily rearranged amplicon, that is, an amplicon that contains amplified segments connected by discordant breakpoint edges suggesting higher-order rearrangements beyond small deletions such as inversions, interchromosomal edges or deletions >1 Mbp; BFB amplicon, that is, an amplicon having a proportion of foldback reads in excess of 25% and which may have signatures of heavily rearranged or circular amplification; circular amplicon, that is, an amplicon that contains one or more genomic segments forming a cyclic path of at least 10 kbp and 4+ copies. b, Left: comparison of WGS-derived circular DNA amplicon and CIRCLE-seq-derived segments. Right: circular amplicons detected from WGS with AmpliconArchitect were validated with CIRCLE-seq. (Cover image from ref1)
![]()
Fig. 2: Oncogene content and structural component of circular amplification. a, Genome-wide distribution of amplification peaks by amplicon class. Amplifications were counted per 1 Mb bin and are shown as a fraction of the total number of samples per amplicon class. b, Classification of amplification status by gene. The 24 most frequently amplified oncogenes are shown. (from ref1)
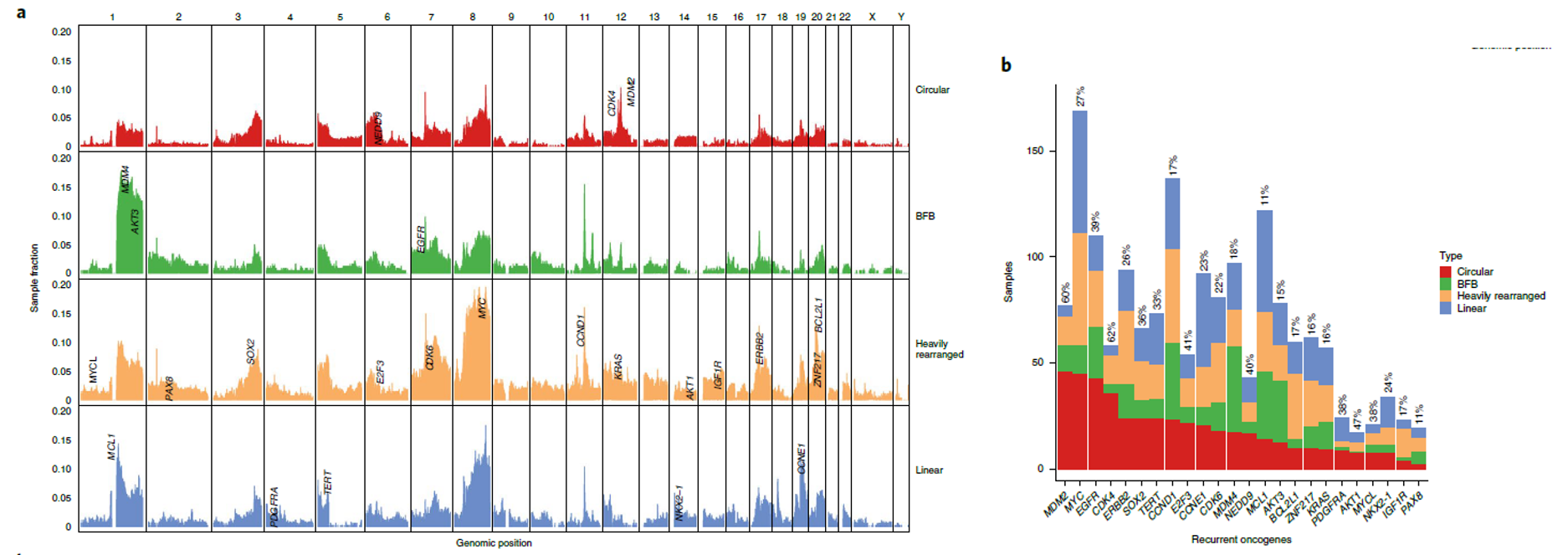
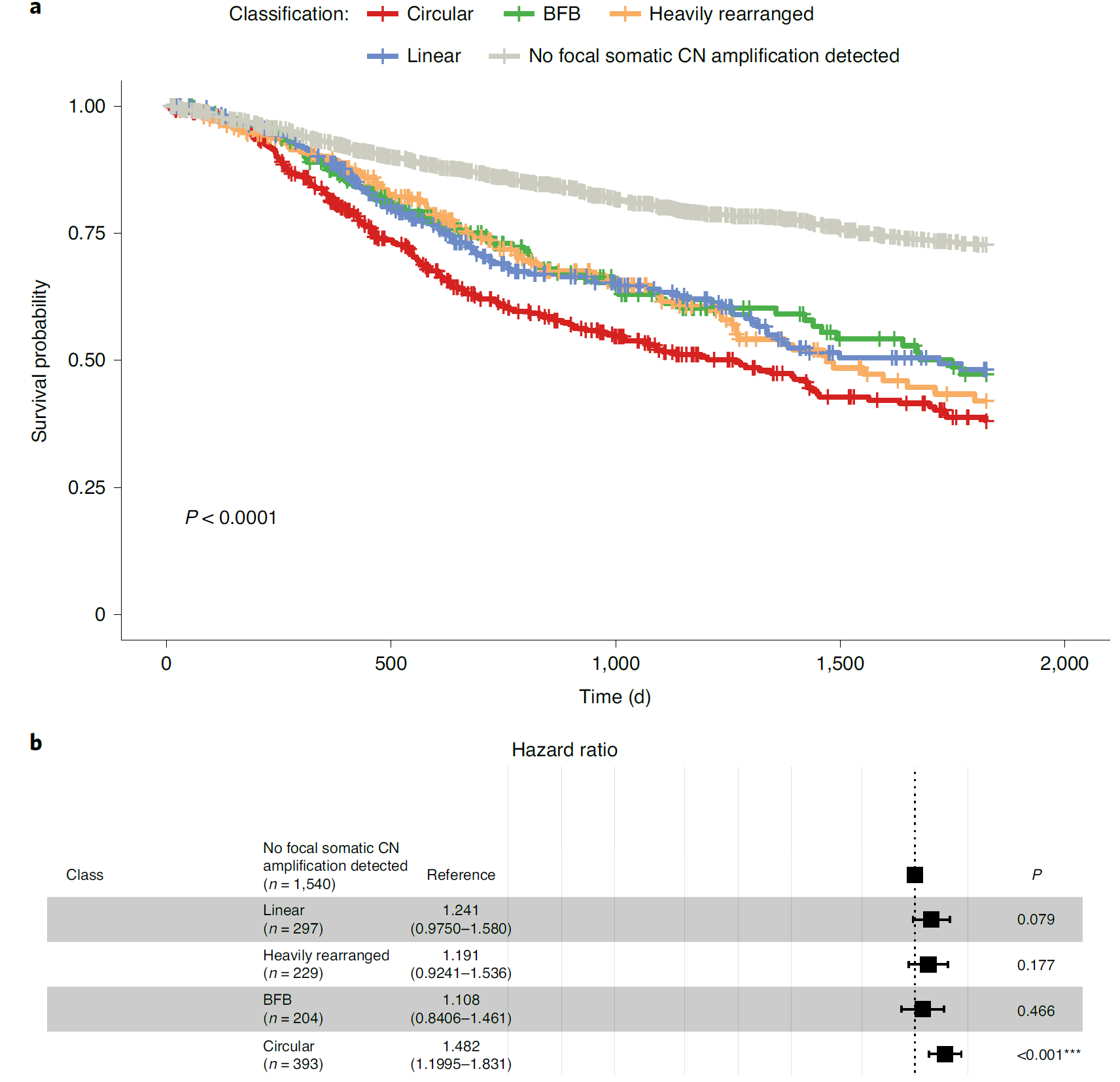
Fig. 3: Presence of circular amplification is associated with poor outcomes. a, Kaplan–Meier 5-year survival curves by amplification category. Patients whose tumors contained at least one circular amplicon had significantly worse outcomes compared to patients whose tumors were classified as noncircular. The P-value derived from comparing the survival curves was based on a log-rank test. b, Multivariate Cox proportional-hazards model, incorporating disease and patient cohorts as the parameters, showing that circular amplification resulted in significantly higher hazard ratios. The error bars represent the 95% confidence intervals of the hazard ratios.
Quick Biology is an expert in Whole genome sequencing and NGS data mining. Find More at Quick Biology.
Ref:
1. Kim, H. et al. Extrachromosomal DNA is associated with oncogene amplification and poor outcome across multiple cancers. Nat. Genet. 52, (2020).